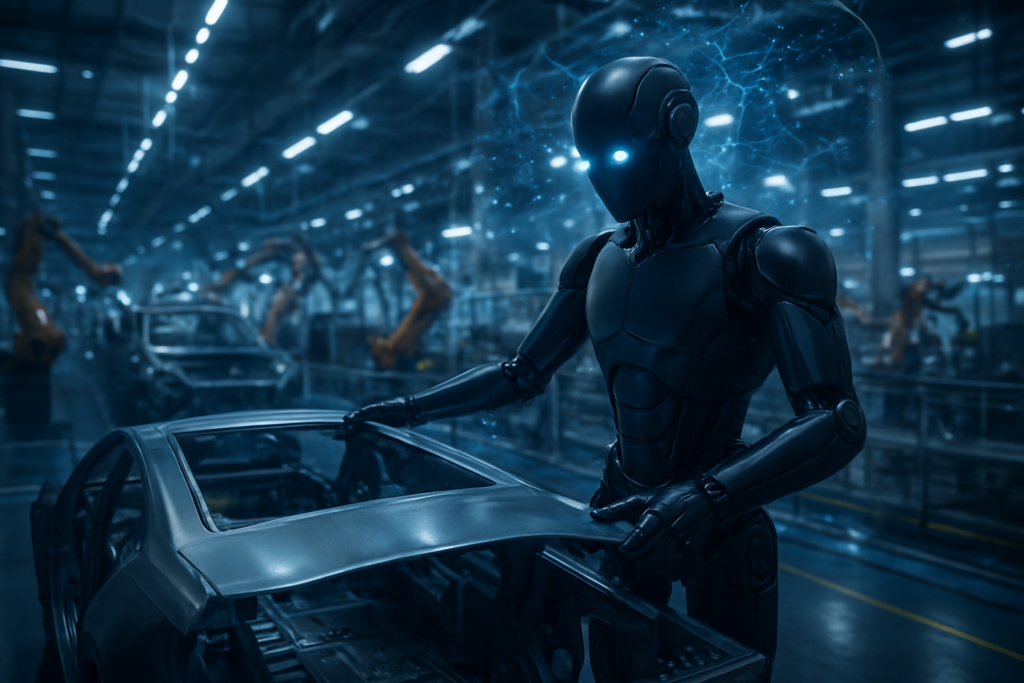
The industrial world has officially crossed the Rubicon from experimental automation to autonomous humanoid labor. In a milestone that has sent ripples through both the automotive and artificial intelligence sectors, Figure AI has concluded its landmark deployment of the Figure 02 humanoid robot at the BMW Group (BMWYY) Plant Spartanburg. Over the course of a multi-month trial ending in late 2025, the fleet of robots transitioned from simple testing to operating full 10-hour shifts on the assembly line, proving that "Physical AI" is no longer a futuristic concept but a functional industrial reality.
This deployment represents the first time a humanoid robot has been successfully integrated into a high-volume manufacturing environment with the endurance and precision required for automotive production. By the time the pilot concluded, the Figure 02 units had successfully loaded over 90,000 parts onto the production line, contributing to the assembly of more than 30,000 BMW X3 vehicles. The success of this program has served as a catalyst for the "Physical AI" boom of early 2026, shifting the global conversation from large language models (LLMs) to large behavior models.
The Mechanics of Precision: Humanoid Endurance on the Line
Technically, the Figure 02 represents a massive leap over previous iterations of humanoid hardware. While earlier robots were often relegated to "teleoperation" or scripted movements, Figure 02 utilized a proprietary Vision-Language-Action (VLA) model—often referred to as "Helix"—to navigate the complexities of the factory floor. The robot’s primary task involved sheet-metal loading, a physically demanding job that requires picking heavy, awkward parts and placing them into welding fixtures with a millimeter-precision tolerance of 5mm.
What sets this achievement apart is the speed and reliability of the execution. Each part placement had to occur within a strict two-second window of a 37-second total cycle time. Unlike traditional industrial arms that are bolted to the floor and programmed for a single repetitive motion, Figure 02 used its humanoid form factor and onboard AI to adjust to slight variations in part positioning in real-time. Industry experts have noted that Figure 02’s ability to maintain a >99% placement accuracy over 10-hour shifts (and even 20-hour double-shifts in late-stage trials) effectively solves the "long tail" of robotics—the unpredictable edge cases that have historically broken automated systems.
A New Arms Race: The Business of Physical Intelligence
The success at Spartanburg has triggered an aggressive strategic shift among tech giants and manufacturers. Tesla (TSLA) has already responded by ramping up its internal deployment of the Optimus robot, with reports indicating over 50,000 units are now active across its Gigafactories. Meanwhile, NVIDIA (NVDA) has solidified its position as the "brains" of the industry with the release of its Cosmos world models, which allow robots like Figure’s to simulate physical outcomes in milliseconds before executing them.
The competitive landscape is no longer just about who has the best chatbot, but who can most effectively bridge the "sim-to-real" gap. Companies like Microsoft (MSFT) and Amazon (AMZN), both early investors in Figure AI, are now looking to integrate these physical agents into their logistics and cloud infrastructures. For BMW, the pilot wasn't just about labor replacement; it was about "future-proofing" their workforce against demographic shifts and labor shortages. The strategic advantage now lies with firms that can deploy general-purpose robots that do not require expensive, specialized retooling of factories.
Beyond the Factory: The Broader Implications of Physical AI
The Figure 02 deployment fits into a broader trend where AI is escaping the confines of screens and entering the three-dimensional world. This shift, termed Physical AI, represents the convergence of generative reasoning and robotic actuation. By early 2026, we are seeing the "ChatGPT moment" for robotics, where machines are beginning to understand natural language instructions like "clean up this spill" or "sort these defective parts" without explicit step-by-step coding.
However, this rapid industrialization has raised significant concerns regarding safety and regulation. The European AI Act, which sees major compliance deadlines in August 2026, has forced companies to implement rigorous "kill-switch" protocols and transparent fault-reporting for high-risk autonomous systems. Comparisons are being drawn to the early days of the assembly line; just as Henry Ford’s innovations redefined the 20th-century economy, Physical AI is poised to redefine 21st-century labor, prompting intense debates over job displacement and the need for new safety standards in human-robot collaborative environments.
The Road Ahead: From Factories to Front Doors
Looking toward the remainder of 2026 and into 2027, the focus is shifting toward "Figure 03" and the commercialization of humanoid robots for non-industrial settings. Figure AI has already teased a third-generation model designed for even higher volumes and higher-speed manufacturing. Simultaneously, companies like 1X are beginning to deliver their "NEO" humanoids to residential customers, marking the first serious attempt at a home-care robot powered by the same VLA foundations as Figure 02.
Experts predict that the next challenge will be "biomimetic sensing"—giving robots the ability to feel texture and pressure as humans do. This will allow Physical AI to move from heavy sheet metal to delicate tasks like assembly of electronics or elderly care. As production scales and the cost per unit drops, the barrier to entry for small-to-medium enterprises will vanish, potentially leading to a "Robotics-as-a-Service" (RaaS) model that could disrupt the entire global supply chain.
Closing the Loop on a Milestone
The Figure 02 deployment at BMW will likely be remembered as the moment the "humanoid dream" became a measurable industrial metric. By proving that a robot could handle 90,000 parts with the endurance of a human worker and the precision of a machine, Figure AI has set the gold standard for the industry. It is a testament to how far generative AI has come, moving from generating text to generating physical work.
As we move deeper into 2026, watch for the results of Tesla's (TSLA) first external Optimus sales and the integration of NVIDIA’s (NVDA) Isaac Lab-Arena for standardized robot benchmarking. The machines have left the lab, they have survived the factory floor, and they are now ready for the world at large.
This content is intended for informational purposes only and represents analysis of current AI developments.
TokenRing AI delivers enterprise-grade solutions for multi-agent AI workflow orchestration, AI-powered development tools, and seamless remote collaboration platforms.
For more information, visit https://www.tokenring.ai/.



